Economics of the Internet
Combinatorial innovation refers to the development of technology that consists of many combinable components that allow for rapid innovation and development.
Categories of Online Economy
Digital goods
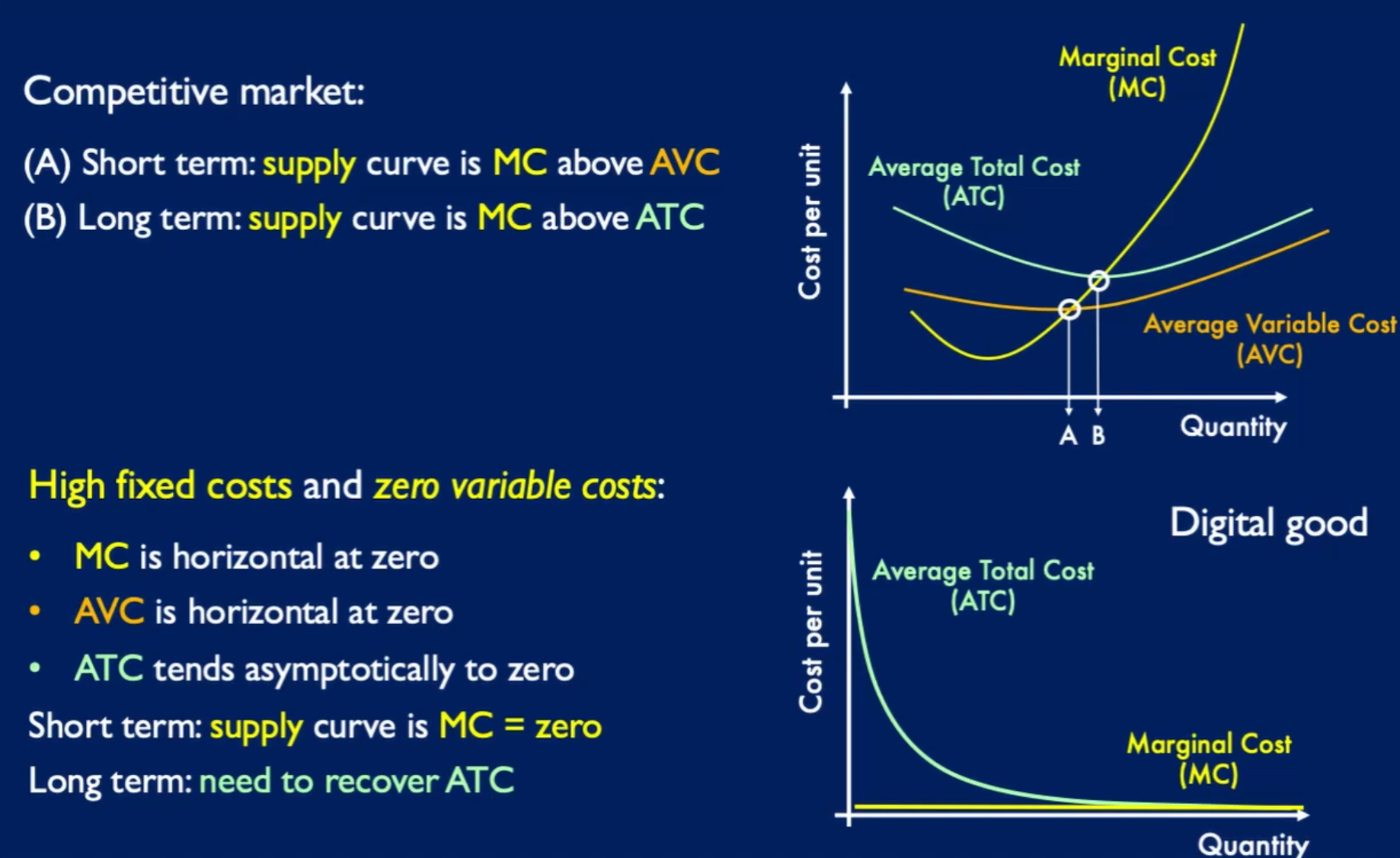
Can be delivered online, but used locally e.g. mp3 files.
- Typically expensive to product, but cheap to reproduce. Most of the production costs cannot be recovered - unlike e.g. you can sell a factory.
- No capacity restraints to reproduction.
- Often experience goods, that is the customer does not know the value of the product until they have used it.
- Search costs for consumers are very low.
- Network Externalities is often strong.
Information goods
Value of the good is in the information it provides e.g. online news.
Online purchasing of physical goods
Online provision of services
E.g. Netflix
Effect of the internet on the decisions of consumers
If the production and consumption of a good/service affects a third party who was not involved in the transaction, we say there is an externality.
A negative externality implies costs on others, e.g. pollution from a factory.
A positive externality implies benefits on others, e.g. education makes a more informed society.
Switching Costs and Lock-in
Digital goods often have higher switching costs than physical goods. Switching costs can include:
- Training how to use the new system
- Network Effect - may need to convince others to join
- Setup costs
- Reduced information on you by new provider compared to old - e.g. Netflix recommendations
Effect of the internet on the decisions of producers
 For commodity digital goods there is a tendency towards monopoly due to:
For commodity digital goods there is a tendency towards monopoly due to:
- New companies will typically have higher unit costs than existing companies due to fewer customers to split fixed costs among
- The Network Effect means the new product must reach critical mass or fail
- Switching costs and lock-in make it difficult to steal users Therefore, for a business to succeed, market differentiation is very important. This means innovation can be more important than efficiency.
Producers take steps to hold a monopoly such as:
- Proprietary file formats
Economics of Standards
Standards reduce the tendency to monopolise due to allowing a user network to be shared between providers. This may seem like a bad business move as it allows competitors to use your network, but it also allows the reverse. Overall the network’s value is increased, bringing in more customers overall, increasing the market as a whole.
Standards Leader
One player often the major player, sets the standard by opening their proprietary format (e.g. PDF)
Standards War
Two or more players compete to determine which standard is adopted.
Standards Negotiation
Players negotiate a standard collectively.
Cards
Q: What is combinatorial innovation? A: The development of technology that consists many combinable components that allow for rapid innovation and development.
Q: What are the categories of online economy? A: - Digital goods - delivered online but used locally
- Information goods - value is the information it provides - e.g. news
- Online purchasing of physical goods
- Online provision of services - e.g. Netflix
Q: Why do commodity digital goods tend towards monopoly? A: - New companies typically have higher unit costs due to fewer customers to split fixed costs among.
- Network effect means new products must reach critical mass or fail
- Switching costs and lock-in make it difficult to steal customers from the monopoly.
Q: What are the three main ways in which standards are created? A: - Standards Leader - One major player sets the standard by opening their proprietary format (e.g. PDF)
- Standards War - Multiple players compete
- Standards Negotiation - Players collectively negotiate
Q: What are the economic benefits of standardisation? A: Despite reducing the ability to monopolise by allowing competitors to use your network, it also allows the reverse. This increases the network’s overall value, bringing in more customers, and increasing the market as a whole.